Hosted Exchange Version Migration
Overview
Atria supports multi-Exchange version coexistence. There will be a time where you may want to upgrade/migrate a customer’s assigned version to a higher one.
This article gives an overview of how Atria interacts with Exchange, considerations for upgrade and how the migration/upgrade is handled through the platform.
Managed Exchange Objects
With Atria’s Hosted Exchange service, the following Exchange objects are managed:
- Mailboxes (Users, Resources)
- Addresses (Address List, Offline Address Book)
- Contacts
- Distribution Groups
- Public Folders
Atria also manages org-wide configuration like Mail Disclaimers, Active Sync Policies, and Mailbox permissions. These are not impacted by the migration process as they are actively pulled from Exchange configuration.
Mailboxes
User Mailbox
In Atria, user mailboxes are tracked in the database by noting whether the service is provisioned and which User Plan is assigned.
During provisioning, Atria checks Exchange for the mailbox using this recorded info. It can detect if the mailbox is being moved, has been deleted, or is restorable (if Recover Mailbox is enabled). If found, Atria re-applies all settings automatically.
A key factor is the version and datastores defined in the User Plan. If the mailbox is not on one of the allowed datastores, Atria will trigger a move to a valid one. For mailboxes with data, this can significantly increase provisioning time and will be logged as a mailbox move.
When migrating between Exchange versions, it’s recommended to move mailboxes using Exchange directly—this supports parallel moves and avoids Atria’s slower, sequential process.
Resource Mailbox
When a Resource Mailbox is created in the portal, its details are saved to the database and sent to the Exchange web service for processing.
During provisioning, the platform checks Exchange for the mailbox using this information. It’s important to ensure the correct version and datastores are set in the Resource Mailbox Datastores. Like user mailboxes, Atria manages which datastores are allowed. If the mailbox is found on an unapproved datastore, it will be moved automatically.
As with user mailboxes, it’s recommended to move resource mailboxes using Exchange.
Addresses
Address List
- Stored in AD, not Atria DB.
- Managed via AD commands.
- No migration needed.
Offline Address List (OAB)
- Exchange 2010: OABs are generated by “OAB Generation Server.”
- Exchange 2013–2019: Created by “Exchange System Mailbox.”
- Migrating from 2010? OABs must be recreated.
Contacts & Distribution Groups
- Stored in AD.
- No migration required.
Public Folders
- Tracked in DB.
- Exchange 2013–2019 use Modern PFs (mailbox infrastructure) — these are interchangeable.
- 2010 PFs must be migrated.
Migration Process
Thanks to Exchange’s coexistence capabilities, migrations can be done gradually. Below is an overview of the migration steps in the context of Atria.
This process requires the Atria Hosted Exchange web service to be installed on the new Exchange server and the Server Connection has been created and tested in the portal.
Update the Hosted Exchange Service Settings
List new objects; Resource Mailbox Datastore, Offline Address Book Server and Public Folders Servers
- Navigate to:
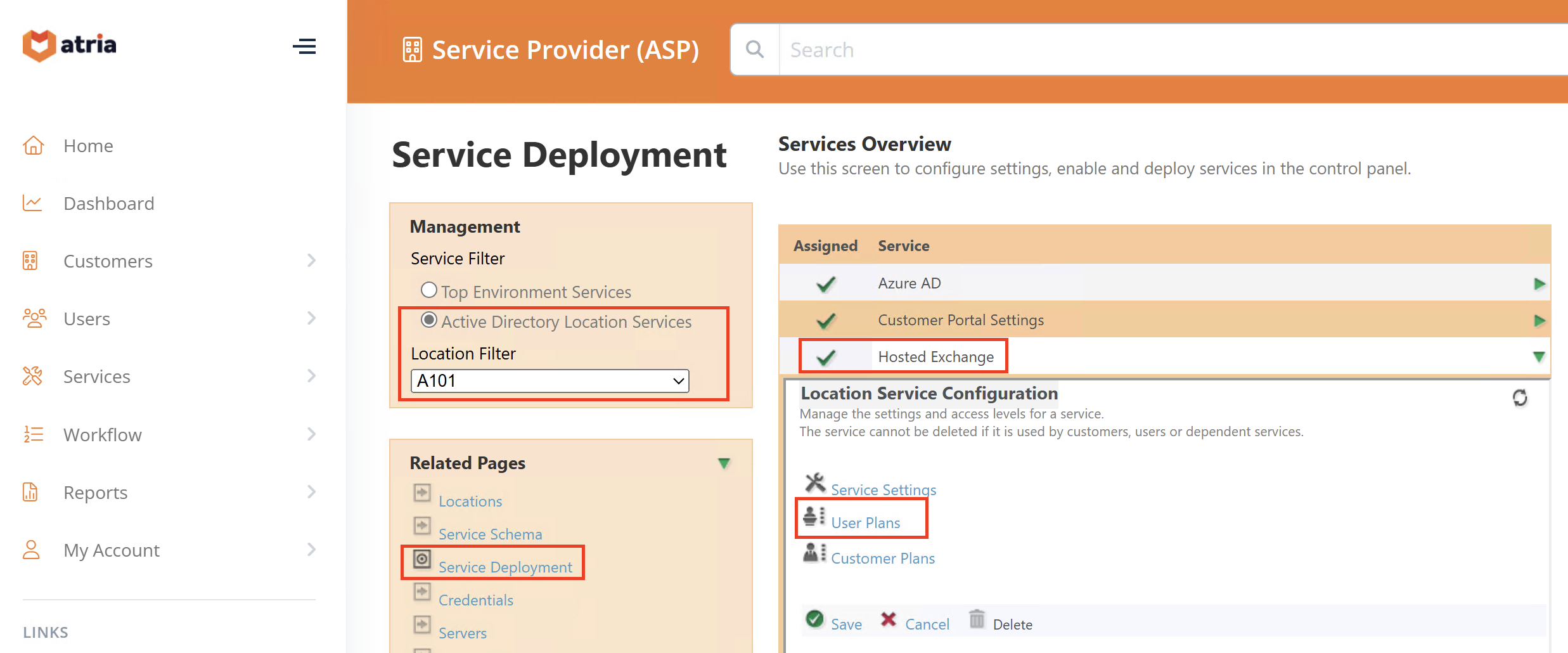
Configuration > Service Deployment > Active Directory Location Service > Hosted Exchange > Service Settings
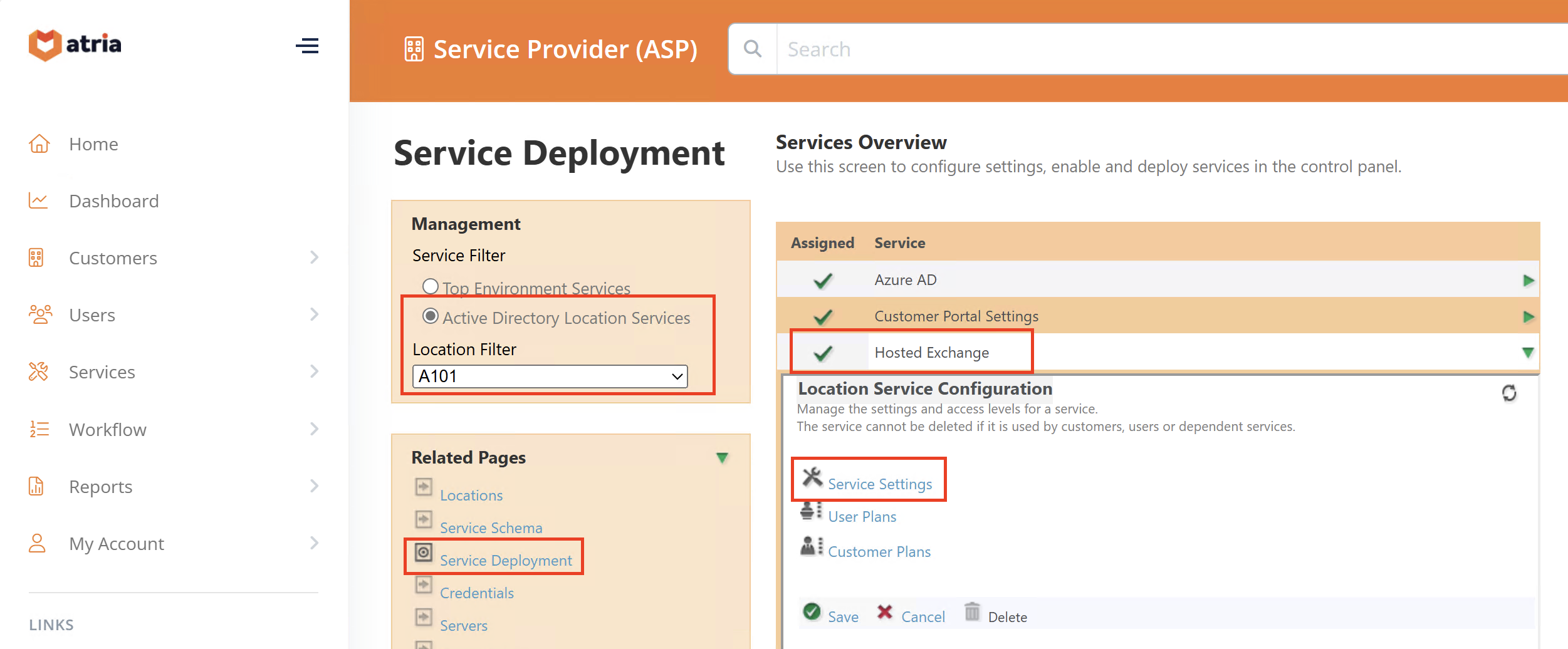
- In Resource MB Mail Databases, reload and select new datastores.
- Available datastores will appear in the white box.
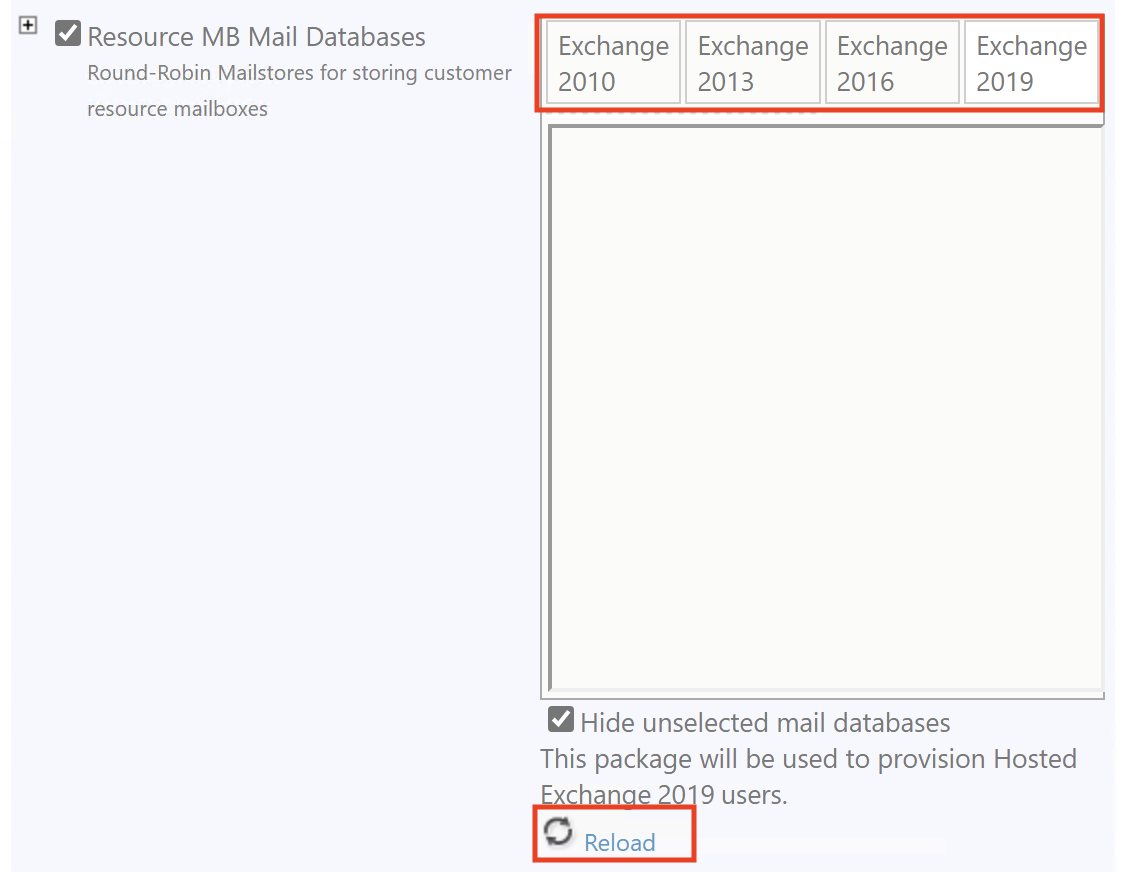
- In Offline Address Book (OAB), reload and select a new Exchange server.
- Available servers will appear above the Reload button.
- In Public Folders, reload and select server (if used).
- Available servers will appear above the Reload button.
Create New User Plans
New User Plans need to be created to represent the new Exchange version. The main difference is referencing the new Exchange Server Mailstores.
- Navigate to:
Configuration > Service Deployment > Top Environment Services > Hosted Exchange > User Plans
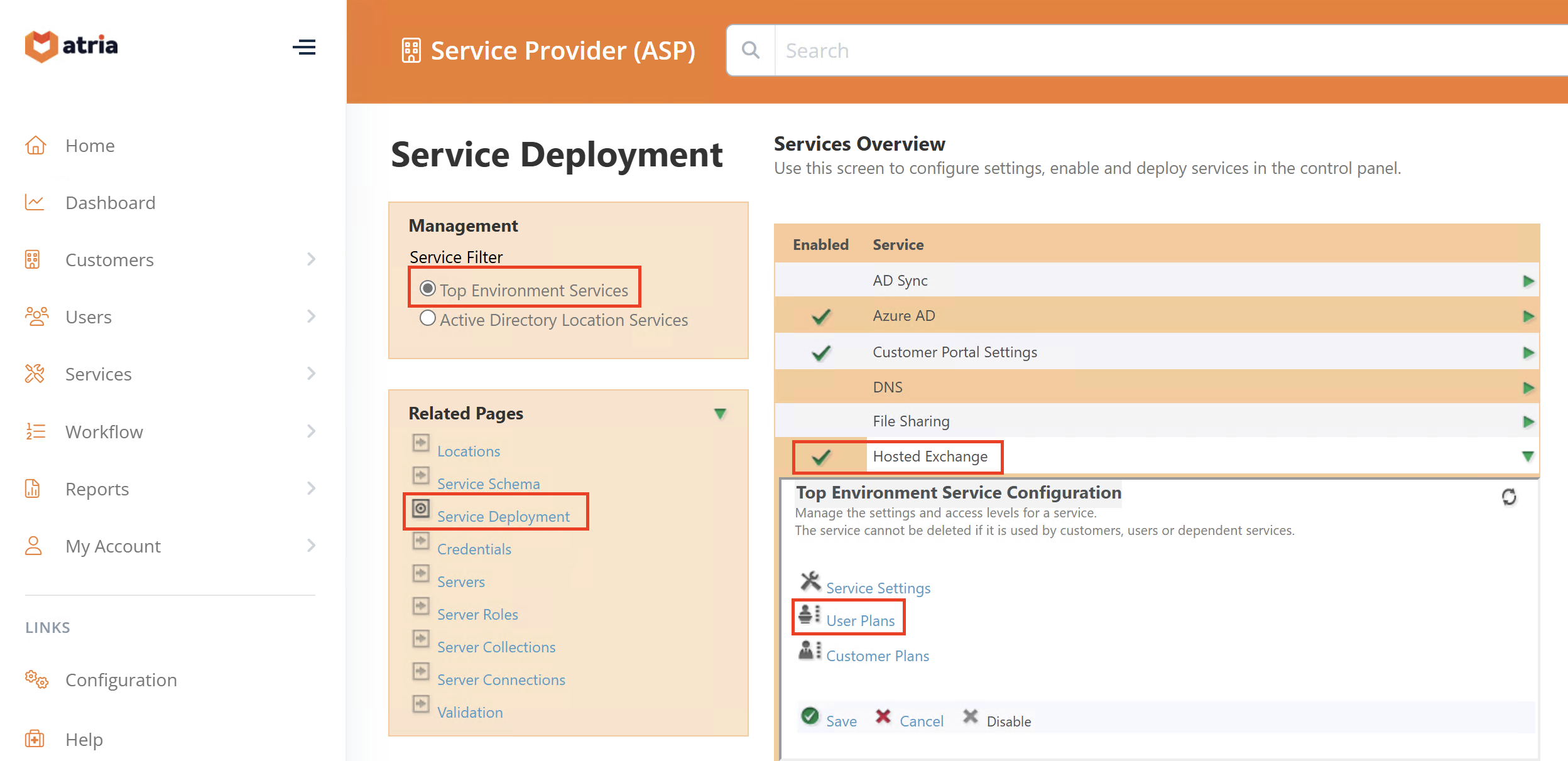
- Create new plans referencing new Mailstores.
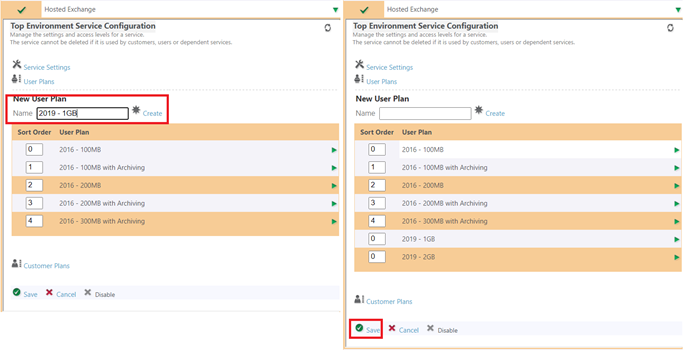
- Switch to Active Directory Location Services and modify your User Plan.
- Most important setting here is the Mail Databases. Click Reload to query available datastores.

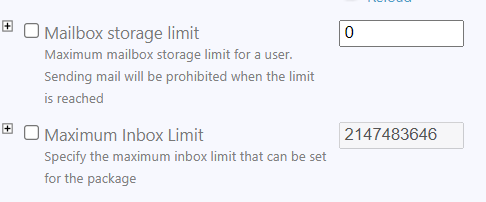
- Set Storage limits as needed.
Migrate the Customer
Move User Mailboxes
As noted under Managed Exchange Objects, it’s recommended to move mailboxes using Exchange for optimal performance.
When creating a move request, pay close attention to the destination datastore. It must match one of the datastores selected in the target User Plan. If the mailbox is moved to an unapproved datastore, the platform will automatically relocate it to one of the approved datastores defined by the User Plan.
Recreate OABs (if coming from Exchange 2010)
A mailbox recreation script is available upon request. Please contact support@getatria.com if needed.
Re-Provision Hosted Exchange
- Navigate to:
Customer > Services > Hosted Exchange
- Select the new version.
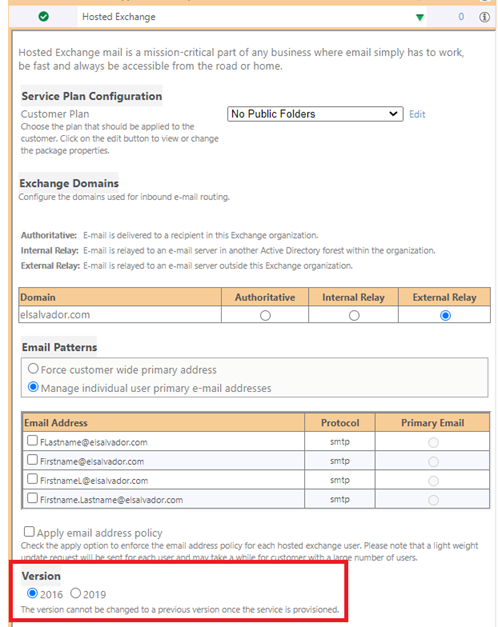
You cannot downgrade after selecting a newer version.
- If the mailbox was previously moved to a datastore defined in the User Plan, the provisioning request will simply reapply the settings and update the version in the database.
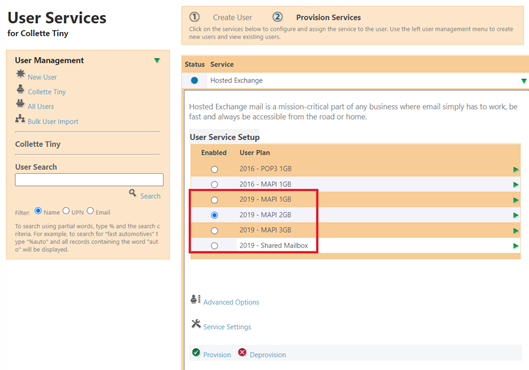
Use Package Migration Wizard
- Navigate to:
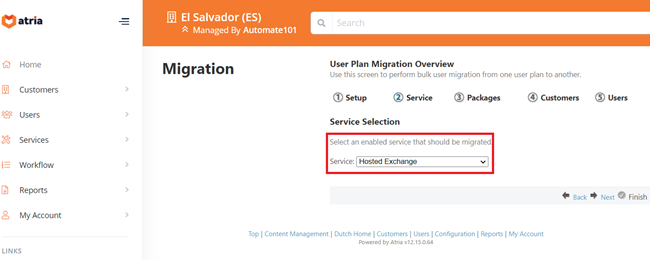
Configuration > Package Migration Wizard
- Select Hosted Exchange
- Choose source/destination User Plans
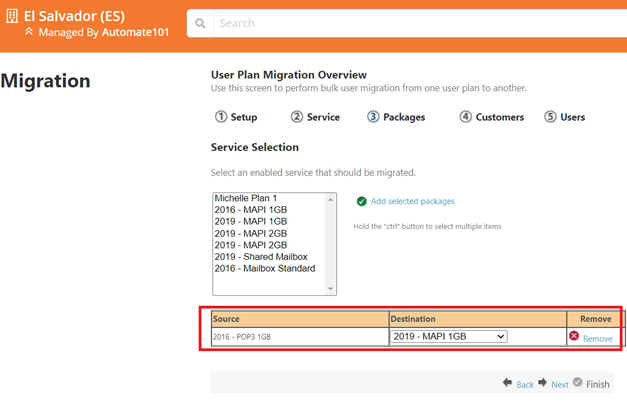
- Select the Customer you want to migrate
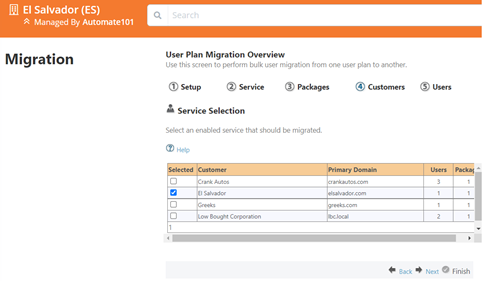
- You can expand
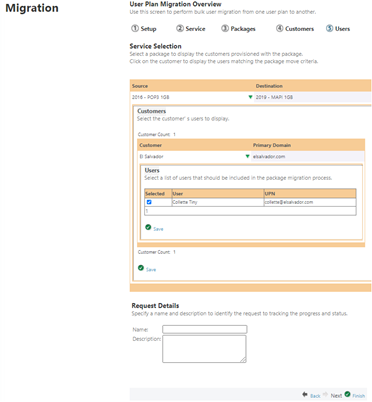
Plan > Customer > Usersto select which of the listed users you want to migrate
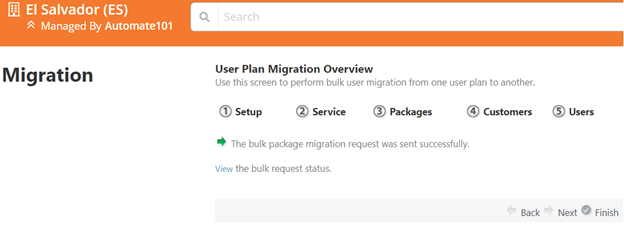
- The page that shows the bulk provisioning request has been sent
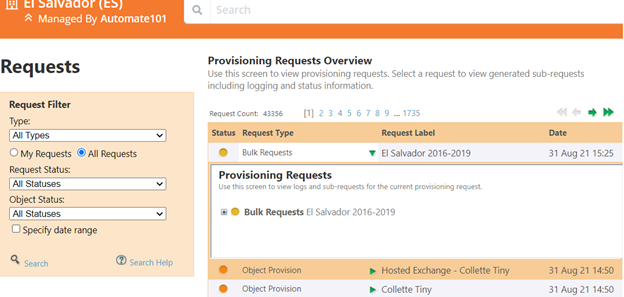
- You can go to Provisioning Request logs to see the created Bulk Request and view its status
Finalize the Migration
Move Public Folders
This step should be performed only after all customers on the platform have been fully migrated.
For Exchange 2013–2019, modern Public Folders are used. In this model, you migrate the Public Folder mailboxes, not the individual content.
For Exchange 2010, Public Folders are stored differently. Here, you must migrate the contents rather than the mailboxes.
Decommissioning Exchange Servers
Atria manages only the objects available within Exchange. Coexistence and interoperability between Exchange versions are handled by Exchange itself. As explained in Manage Exchange Objects, this is how the platform locates and processes provisioning requests.
Before decommissioning an older Exchange version, ensure that system components such as Arbitration or System Mailboxes have been properly reviewed and migrated.